What is Bitcoin blockchain?
The blockchain functions as a decentralized and publicly accessible ledger, meticulously recording the complete history of every bitcoin transaction. Any individual can procure a copy of the blockchain, affording them the opportunity to scrutinize its contents and trace the trajectory of bitcoins from one transaction to the next.
It’s crucial to recognize that while the blockchain meticulously documents every bitcoin transaction, these transactions remain detached from real-life identities. Consequently, Bitcoin operates under the concept of pseudonymity, safeguarding users’ privacy.

Contrary to conventional files stored on a computer’s hard drive, bitcoins do not exist in tangible form. Instead, “owning bitcoins” equates to possessing a bitcoin address, with its corresponding balance recorded within the blockchain. To possess a bitcoin address entails maintaining control over the associated Private Key, enabling the authorization and signing of transactions.
This decentralized approach to ownership underscores Bitcoin’s fundamental principle of user autonomy and security, as users retain exclusive control over their digital assets.
What is a block?
A Block represents a collection of Bitcoin transactions conducted within a specific timeframe. These Blocks are arranged in a sequential manner, with each subsequent Block building upon the preceding one. This interconnectedness forms a continuous chain of Blocks, hence the term “blockchain.”
Bitcoin miners engage in the task of discovering and disseminating new Blocks in order to earn bitcoins. Approximately every 10 minutes, a new Block is broadcasted, rewarding the miner who successfully solved it with a quantity of bitcoins. The role of Bitcoin miners is paramount in upholding network security, as they validate transactions and safeguard the blockchain against fraudulent activities.
When waiting for a new bitcoin transaction to be confirmed, individuals are essentially awaiting the publication of a new Block containing their transaction. Once included in a Block, the bitcoin network deems the transaction as valid.
Various Bitcoin services may impose different requirements for transaction finalization; for instance, Coinbase typically mandates three network confirmations before considering a transaction as fully executed. However, these confirmation standards may vary across different platforms within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
How does blockchain work?
If you’re familiar with spreadsheets or databases, understanding a blockchain’s functionality becomes more accessible. Like traditional databases or spreadsheets, a blockchain serves as a repository for entering and storing information. However, the distinguishing feature lies in how the data is structured and accessed within a blockchain.
Within a blockchain, there are programs referred to as scripts, which perform functions akin to those executed in a database—such as data entry, access, and storage. What sets a blockchain apart is its decentralized nature; multiple copies of the blockchain are stored across numerous machines, with each copy required to match for validation.
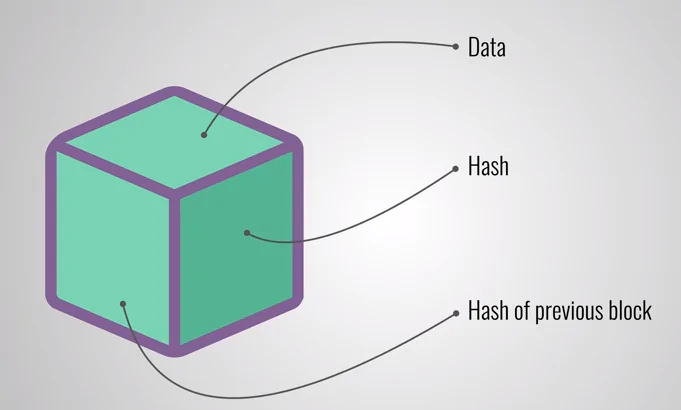
Transactions are compiled within the blockchain and organized into blocks, analogous to cells in a spreadsheet housing information. When a block reaches its capacity, the data undergoes encryption through an algorithm, resulting in the generation of a hexadecimal number known as the hash.
Subsequently, this hash is integrated into the header of the subsequent block, where it undergoes encryption alongside other block information. This iterative process generates a chain of interconnected blocks, hence the term “blockchain.” This sequential chaining ensures the integrity and immutability of the stored data within the blockchain network.